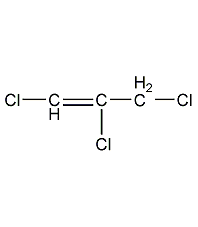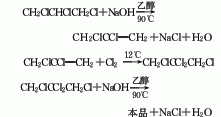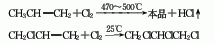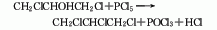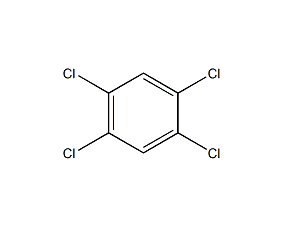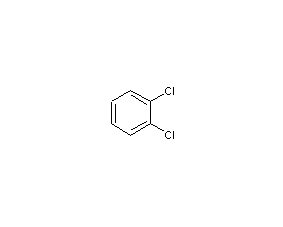
structural formula
| physical competition number |
0297 |
| molecular formula |
c6h4cl2 |
| molecular weight |
147.00 |
| label |
o-dichlorobenzene,
o-dichlorobenzene,
aromatic halogen derivatives,
liquid crystal materials and intermediates
|
numbering system
cas number:95-50-1
mdl number:mfcd00000535
einecs number:202-425-9
rtecs number:cz4500000
brn number:606078
pubchem number:24854428
physical property data
1. properties: colorless and volatile liquid with aromatic smell. [1]
2. melting point (℃): -17.5[2]
3. boiling point (℃): 180.4[3]
4. relative density (water = 1): 1.30[4]
5. relative vapor density (air=1): 5.05[5]
6. saturated vapor pressure (kpa): 0.133 (20℃)[6]
7. heat of combustion (kj/mol): -2725.38[7]
8. critical temperature (℃): 417.2[8]
9. critical pressure (mpa): 4.03[9]
10. octanol/water partition coefficient: 3.43 [10]
11. flash point (℃): 66 (cc); 68 (oc) [11]
12. ignition temperature (℃): 647[12]
13. explosion limit (%): 9.2[13]
14. lower explosion limit (%): 2[14]
15. solubility: insoluble in water, soluble in most organic solvents such as ethanol, ether, and benzene. [15]
16. viscosity (mpa·s, 25ºc): 1.324
17. flash point (ºc, closed): 66.1
18. flash point (ºc, open): 73.9
19. fire point (ºc): 648
20. heat of vaporization (kj/mol, b.p.): 39.69
21. heat of fusion (kj/mol): 12.60
22. heat of formation (kj/mol): 18.42
23. heat of combustion (kj/ mol, 25ºc, liquid): 2964.13
24. specific heat capacity (kj/(kg·k), 0ºc, liquid): 1.13
25. electrical conductivity (s/m, 25ºc ): 3×10-11
26. solubility (%, water, 20ºc): 0.0134
27. volume expansion coefficient (k -1, 20ºc): 0.00085
28. relative density (25℃, 4℃): 1.3007
29. refractive index at room temperature (n25): 1.527870
30. solubility parameter (j·cm-3)0.5: 20.311
31.van der waals area (cm2·mol-1): 8.220×109
32. van der waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 87.300
33. liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy )( kj·mol-1): -17.5
34. liquid phase standard hot melt (j·mol-1·k -1): 170.9
35. the gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kj·mol-1): 30.2
36. gas phase standard entropy (j·mol-1·k-1): 341.96
37. gas phase standard formation free energy (kj·mol-1): 83.0
38. gas phase standard hot melt (j·mol-1·k-1): 113.43
toxicological data
1. acute toxicity:
mouse oral lc5o: 4386mg/kg; rat oral ld50: 500mg/kg; rabbitoral ld5o of children: 500mg/kg; oral ldlo of guinea pigs: 2000mg/kg; transdermal ld5o of rabbits: >10000mg/kg; inhalation lclo of guinea pigs: 800ppm/24h; inhalation ldlo of rats: 821ppm/7h;
2. acute toxicity[16]
ld50: 500mg/kg (rat oral); >10g/kg (rabbit dermal )
lc50: 8150mg/m3 (rat inhalation, 4h)
3. irritation [17] sup> rabbit eye: 100mg (30s), slight irritation.
4. subacute and chronic toxicity [18] rats were orally administered 30~50 mg/kg of o-dichlorobenzene, 5 days a week. for a total of 13 weeks, the results showed that in the 50 mg/kg exposure group, the rats’ weight decreased, urinary porphyrin excretion increased, and the liver/body ratio increased. pathology shows degeneration and necrosis of the central lobules of the liver and epithelial degeneration of the renal epithelium.
5. mutagenicity [19] gene transformation and mitotic recombination: saccharomyces cerevisiae 1mmol/l. sperm morphology: rats were given 250 mg/kg intraperitoneally. micronucleus test: mice were given 187mg/kg intraperitoneally (24h). microbial mutagenicity: mouse lymphocytes 6500 μg/l. sister chromatid exchange: hamster ovary 59mg/l
6. teratogenicity[20] the lowest inhalation toxicity in rats is 6~15 days after pregnancy. the dose (tclo) is 200ppm (6h), causing developmental malformation of the musculoskeletal system.
ecological data
1. ecotoxicity[21]
lc50: 9.4~100mg/l (96h) (fish)
ic50: 53~100mg/l (72h) (algae)
2. biodegradability[22]
aerobic biodegradation (h): 672~4320
anaerobic biodegradation (h): 2880~17280
3. non-biodegradability[23 ]
photolysis maximum light absorption wavelength range (nm): 219.5~269
photooxidation half-life in air (h): 152.8~1528
first-grade hydrolysis half-life (h): >879a
4. other harmful effects[24] this substance is harmful to the environment , can cause pollution to water bodies and the atmosphere, and bioaccumulate in food chains important to humans, especially in aquatic organisms.
molecular structure data
1. molar refractive index: 36.04
2. molar volume (cm3/mol): 113.3
3. isotonic specific volume (90.2k ): 279.0
4. surface tension (dyne/cm): 36.7
5. dielectric constant:
6. dipole moment (10-24cm3 ):
7. polarizability: 14.28
compute chemical data
1. reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (xlogp): none
2. number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 0
4. number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. number of tautomers: none
6. topological molecule polar surface area 0
7. number of heavy atoms: 8
8. surface charge: 0
9. complexity: 62.9
10. number of isotope atoms: 0
11. determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. number of covalent bond units: 1
properties and stability
1. under the action of moisture and light, trace amounts of highly corrosive hydrogen chloride are released. highly corrosive to rubber. alkaline hydrolysis does not occur at room temperature. using copper or copper salt as catalyst under high temperature and high pressure, alkaline hydrolysis generates o-chlorophenol. it reacts with ammonia to form o-chloroaniline at 200°c. it reacts with chlorine under the catalysis of ferric chloride to produce 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene and 1,2,3-trichlorobenzene. it reacts with a mixed acid of nitric acid and sulfuric acid to produce 3,4-dichloronitrobenzene. reacts with fuming sulfuric acid to form 3,4-dichlorobenzenesulfonic acid.
2. this product is highly irritating and moderately toxic if swallowed and inhaled. rat oral ld50500mg/kg. the maximum allowable concentration in the air is 50*10-6. the workplace should be well ventilated, the equipment should be sealed, and operators should wear protective equipment.
3. it is more toxic than m-dichlorobenzene and p-dichlorobenzene. inhaling high-concentration vapor can cause central nervous system paralysis, mainly damaging the liver and kidneys. it can irritate the skin and mucous membranes and is easily absorbed by the skin. the olfactory threshold concentration is 305mg/m3. the maximum allowable concentration in the workplace is 300 mg/m3 (united states, japan). the ld50 for intravenous injection into rabbits is 500mg/kg.
4. stability[25] stable
5. incompatible substances[26] strong oxidants, aluminum
6. conditions to avoid contact[27] humid air, heat
7. polymerization hazard[28] no polymerization
8. decomposition products[29] hydrogen chloride
storage method
1. storage precautions[30] store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. keep away from fire and heat sources. keep container tightly sealed. they should be stored separately from oxidants, aluminum, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. the storage area should be equipped with leakage emergency response equipment and suitable containment materials.
2. packed in iron drums, 200kg per drum. during storage and transportation, be sure to be shockproof, sunproof, fireproof, moistureproof, and pay attention to safety. store and transport according to regulations on toxic substances.
synthesis method
prepared from chlorobenzene by-product and synthetic method.
1. recycling of chlorobenzene by-products whether chlorobenzene is produced using the benzene liquid-phase chlorination method or the benzene gas-phase oxychlorination method, dichlorobenzene is co-produced. according to the actual demand, the production ratio of monochlorobenzene and dichlorobenzene can be adjusted by changing the chlorination process conditions. according to the current process control conditions and production conditions of chlorobenzene, the ratio of chlorobenzene to dichlorobenzene is 30-35:1. the industrial methods for separating o- and para-dichlorobenzene mainly include distillation and crystallization.
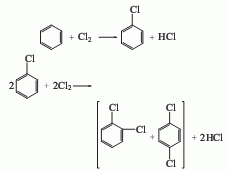
2. from o-chloroaniline via obtained by diazotization and substitution. add o-chloroaniline and hydrochloric acid to the reaction pot and mix evenly below 25°c. cool to 0°c, add sodium nitrite solution dropwise, keep the temperature at 0-5°c, stop adding when the potassium iodide starch solution turns blue, and obtain a diazonium salt solution. add cuprous chloride to the hydrochloric acid solution at 0 to 5°c, stir and mix thoroughly, raise the temperature to 60 to 70°c, react for 1 hour, cool and let stand for layering, and repeatedly add 5% sodium hydroxide and water to the oil layer. wash, dehydrate with anhydrous calcium chloride, fractionate, and collect the 177-183°c fraction to obtain the finished product.

purpose
1. it can be used as a solvent for wax, gum, resin, tar, rubber, oil and asphalt, etc., and is used in the production of dyes shilin black and shilin yellow brown, high-grade pigments, the drug chlorhexidine, and polyurethane raw material tdi. the solvent o-dichlorobenzene is used. this product can be used as an insecticide for termites, locusts, and borers. it can be used in the production of triclofenac, thorastrobin, and xinyanling. it can also be used in the synthesis of catechol, fluorochloroaniline, 3,4 -dichloroaniline and o-phenylenediamine. as an anti-rust agent and degreaser, it can remove carbon and lead from engine parts, remove coatings on metal surfaces without corroding the metal, and remove sulfur from lighting gases.
2. can be used as an ingredient in metal polishing agents; in the dye industry, it is also used to make vat blue clb and vat blue clg; polymer wet spinning solvent to reduce fiber thermal shrinkage; epoxy resin dilution agent, coolant, heat exchange medium; pharmaceutical long-acting sulfa, etc.
3. it has strong dissolving ability, good permeability and slow evaporation rate, so it is used as an additive for nitrocellulose spray paint and varnish and a solvent for wax and tar. also used as a degreasing agent in the metal, leather, automotive, and aircraft industries. a mixture with a small amount of higher alcohol is used as a rust inhibitor. others are also used as intermediates and organic heat carriers in the manufacture of refrigerants, pesticides, fumigants, preservatives, dyes, medicines, etc.
4. used in organic synthesis, dye manufacturing, cleaning agents, and solvents. also used in the preparation of pesticides, cleaning agents and solvents.
5. it is widely used as a solvent and preservative for organic matter and non-ferrous metal oxides, and also as a pesticide. [31]
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/39757extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/1814extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/fascat4351-catalyst-arkema-pmc/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44011extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/dabco-xd-104-dabco-tertiary-amine-catalyst-catalyst-xd-104/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/1776extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/71.jpgextended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/40279extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/category/products/page/47extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/33-13.jpg