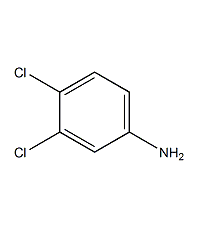
structural formula
| business number |
029s |
| molecular formula |
c6h5cl2n |
| molecular weight |
162 |
| label |
aromatic nitrogen-containing compounds and their derivatives
|
numbering system
cas number:95-76-1
mdl number:mfcd00007768
einecs number:202-448-4
rtecs number:bx2625000
brn number:636837
pubchem number:24867396
physical property data
1. characteristics: brown needle-like crystals. [1]
2. melting point (℃): 70~72.5[2]
3. boiling point (℃) :272[3]
4. relative density (water = 1): 1.33[4]
5. relative vapor density (air=1): 5.59[5]
6. saturated vapor pressure (kpa): 0.13 (80.5℃)[6]
7. critical pressure (mpa): 4.1[7]
8. octanol/water partition coefficient: 2.69[8]
9. flash point (℃): 166 (oc) [9]
10. ignition temperature (℃): 265[10]
11. explosion upper limit (%): 7.2 (179°c) [11]
12. explosion lower limit (%): 2.8 (153℃) [12]
13. solubility: slightly soluble in water, soluble in most organic solvents. [13]
toxicological data
1. acute toxicity[14] ld50: 545mg/kg (rat oral)
2. irritation[15]
rabbit transdermal: 2mg (24h), severe stimulation.
rabbit eye: 250μg (24h), severe irritation.
3. mutagenicity [16] microbial mutagenicity: aspergillus nidulans 200mg/l. sister chromatid exchange: human lymphocytes 125 μmol/l.
ecological data
1. ecotoxicity[17]
lc50: 7.26~8.95mg/l (96h) (fathead minnow, 36d); <0.1mg/l (96h) (daphnia)
2. biodegradability no data available
3. non-biodegradability [18] in the air, when the concentration of hydroxyl radicals is 5.00×105 units/cm3, the degradation half-life is 17h (theory).
4. bioaccumulation [19] bcf: 30.2 (zebrafish, contact time 10h)
molecular structure data
1. molar refractive index: 40.27
2. molar volume (cm3/mol): 115.6
3. isotonic specific volume (90.2k ): 304.8
4. surface tension (dyne/cm): 48.3
5. polarizability (10-24cm3): 15.96
compute chemical data
1. reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (xlogp): none
2. number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. number of tautomers: none
6. topological molecule polar surface area 26
7. number of heavy atoms: 9
8. surface charge: 0
9. complexity: 97.1
10. number of isotope atoms: 0
11. determined number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13.�the number of stereocenters of certain chemical bonds: 0
14. the number of stereocenters of uncertain chemical bonds: 0
15. the number of covalent bond units: 1
properties and stability
1. this product is toxic. can cause lesions in the respiratory system, nervous system and hematopoietic system. mice were given ld501000mg/kg by gavage, and rats were given ld50700mg/kg by gavage. the olfactory threshold of rats is 0.047mg/m3; the lowest light perception of the eyes is 0.025mg/kg. the equipment should be sealed to prevent running, leaking, dripping and leaking. protective equipment should be worn during operation to avoid direct contact with the human body. the maximum allowable concentration in the air in the operating place is 0.05mg/m3.
2. stability[20] stable
3. incompatible substances[21] acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, strong oxidants
4. conditions to avoid contact[22] heating
5. polymerization hazard[23] no polymerization
6. decomposition products[24] hydrogen chloride
storage method
storage precautions[25] store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. keep away from fire and heat sources. the packaging is sealed. they should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
synthesis method
1. using anhydrous ferric chloride as a catalyst, pass chlorine gas into the molten p-nitrochlorobenzene at 105°c to obtain 3,4-dichloronitrobenzene. then, it undergoes reduction reaction with iron powder, formic acid and water under reflux to obtain 3,4-dichloroaniline. 3,4-dichloronitrobenzene can also be obtained by nitration of o-dichlorobenzene. glacial acetic acid can be used instead of formic acid in the reduction reaction with iron powder. another reduction method is catalytic hydrogenation.
2. the preparation method is to add p-chloronitrobenzene and anhydrous ferric chloride catalyst into the reaction kettle, and introduce chlorine gas at 100-110°c. when the freezing point of the chlorination reactant reaches 30 the reaction endpoint is when ~31°c. move this material to the reduction kettle, then add sodium thiosulfate (to eliminate the influence of residual chlorine in the reactant) and formic acid, heat to 100°c (reflux state) and slowly add iron powder (complete addition in about 4 to 5 hours). then continue to maintain the reflux reaction, and the end point of the reaction is when no nitrobenzene is observed. add chlorobenzene with 5 to 6 times the yield of 3,4-dichloroaniline, stir for 0.5 to 1.0 hours, cool, filter and wash the filter residue with a small amount of chlorobenzene. the resulting filtrate is a chlorobenzene solution of 3,4-dichloroaniline. heating and dechlorination of benzene gives 3,4-dichloroaniline.
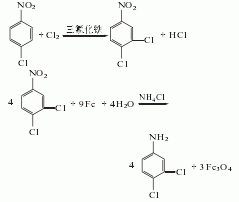
3,4-dichloronitrate can also be used it is prepared by catalytic hydrogenation of benzene. add 3,4-dichloronitrobenzene to the autoclave, add raney nickel catalyst, industrial ethanol as the solvent, flush the high-pressure system with nitrogen 3 times, hydrogen 3 times, then fill with hydrogen to a pressure of 4 mpa, and at the same time the temperature is raised to 60-70°c for reaction until no hydrogen is absorbed, and then the finished product can be obtained by cooling and post-processing.
in addition, o-dichlorobenzene can also be used as raw material, which can be nitrated to obtain 3,4-dichloronitrobenzene, which can then be further reduced to obtain the finished product. most foreign companies use this method to produce 3,4-dichloroaniline.
purpose
1. used to synthesize c.i. disperse red 153 (disperse red g-s) and c.i. disperse red 152, etc. it is also an intermediate for herbicides such as diuron and benzofen.
2. used in dye intermediates, pesticide intermediates and biological component intermediates. [26]
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44765extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/ethylhexanoic-acid-zinc-salt/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/42995extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44567extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/59.jpgextended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/low-atomization-catalyst-9727-low-atomization-amine-catalyst/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/584extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/805extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/nt-cat-ea-103-catalyst-cas10027-40-8-newtopchem/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/n-acetylmorpholine-cas1696-20-4-4-acetylmorpholine/