2,4,4-trimethyl-2-pentanol
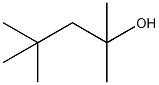

structural formula
| business number | 079e |
|---|---|
| molecular formula | c8h18o |
| molecular weight | 130.23 |
| label |
2-hydroxy-2,4,4-trimethylpentane, aliphatic compounds |
numbering system
cas number:690-37-9
mdl number:mfcd00101611
einecs number:none
rtecs number:none
brn number:none
pubchem id:none
physical property data
1. properties: colorless and transparent liquid.
2. density (g/ml, 25/4℃): 0.819
3. relative density (20℃, 4℃): 0.823
4 . melting point (ºc): undetermined
5. boiling point (ºc, normal pressure): 164.4
6. refractive index at room temperature (n25): 1.426
7. refractive index at room temperature (n20): 1.428
8. flash point (ºc): undetermined
9. specific rotation (º): not determined
10. autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºc): not determined
11. vapor pressure (kpa, 25ºc): not determined determined
12. saturated vapor pressure (kpa, 60ºc): undetermined
13. heat of combustion (kj/mol): undetermined
14. critical temperature (ºc): undetermined
15. critical pressure (kpa): undetermined
16. log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: undetermined
p>
17. explosion upper limit (%, v/v): undetermined
18. explosion lower limit (%, v/v): undetermined
19. dissolution sex: undetermined.
toxicological data
none
ecological data
generally not hazardous to water, do not discharge material into the surrounding environment without government permission.
molecular structure data
1. molar refractive index: 40.57
2. molar volume (cm3/mol): 158.1
3. isotonic specific volume (90.2k ): 357.3
4. surface tension (dyne/cm): 26.0
5. dielectric constant:
6. dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. polarizability: 16.08
compute chemical data
1. reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (xlogp): 2.2
2. number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. number of tautomers: none
6. topological molecule polar surface area 20.2
7. number of heavy atoms: 9
8. surface charge: 0
9. complexity: 87.2
10. number of isotope atoms: 0
11. determine the number of atomic stereocenters�:0
12. uncertain number of stereocenters of atoms: 0
13. determined number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
14. uncertain chemical bonds number of stereocenters: 0
15. number of covalent bond units: 1
properties and stability
keep away from oxides.
storage method
store in an airtight container in a cool, dry place. store away from oxidizing agents. avoid sources of fire.
synthesis method
none
purpose
none